The 5S framework is a systematic approach primarily used in the manufacturing sector to create organized, clean, and efficient workspaces. This method promotes a culture of continuous improvement that enhances productivity and safety. The 5S audit checklist serves as a vital tool in this process, helping businesses maintain the discipline needed to ensure each element of 5S is properly implemented.
Insights
When Training and Work Become One
With businesses facing increasing skills shortages in a tight labor market, the need for effective training and development programs for workers has never been more critical. Traditional approaches such as paper-based training binders or computerized Learning Management Systems (LMS) have been the backbone of corporate training initiatives to date. However, as skills gaps widen and job requirements become more demanding, there is a growing recognition of the limitations of traditional classroom and online learning approaches.
Learning in the flow of work
Microlearning, an approach to delivering bite-sized learning content in short, focused bursts, has caught the attention of most training teams. Its brevity makes it highly accessible and convenient, fitting the modern worker’s shorter attention span. Secondly, microlearning enhances retention and comprehension by presenting information in digestible chunks, allowing learners to absorb and apply knowledge more effectively. A study from Training Magazine found that organizations using microlearning saw a 20% increase in employee productivity and a 23% increase in employee satisfaction.
With today’s mobile digital technologies, microlearning platforms or microlearning apps can deliver content on demand and personalized based on the process, worker activity or experience level. Josh Bersin, a Deloitte Partner and head of their corporate learning practice, wrote an interesting article where he coined the phrase “Learning in the flow of work.” He sees the future of training as fusing microlearning apps into the digital platforms that workers use to get their jobs done. And he points to studies showing that 49% of workers want to consume training at the point of need.
When training and work become one
Reimaging training as a component of the work process not only represents a game-changer in the realm of workforce training and development, but also becomes a driver to bridge the growing skills gaps and boost worker productivity and quality. By weaving training into daily work processes and procedures, organizations can see their training efforts improve in several key areas:
1. Contextual and Situational Relevance
Integrating training into work instruction ensures that learning experiences are directly relevant to worker’s day-to-day responsibilities and tasks. By embedding training content within the context of actual job functions, the workforce can immediately address knowledge and skills gaps at the point of need.
2. Efficient Use of Time and Resources
Digital access to training optimizes the use of time and resources by minimizing disruptions to workflow and productivity. Instant access to training and information when needed maximizes efficiency and minimizes downtime. Instead of allocating separate time slots for training sessions, employees can seamlessly transition between learning and work tasks.
3. Interactive and Engaging Learning Experiences
Digitalized access and embedded microlearning enable more interactive and engaging learning experiences in an on-demand style. Training can engage workers with multimedia and interactivity to deliver a hands-on experience that enhances retention and comprehension, and makes learning more enjoyable and memorable.
It starts by digitalizing the frontline
With increasing skilled labor scarcity and growing job complexity, it is clear that the tools of the frontline workforce need to be modernized. The good news is that today workers are more comfortable with digital apps on mobile devices, and the next generation of frontline workers expect these types of resources to be available to them on the job. Particularly in manufacturing and field services, where replacing paper with mobile devices to enable more efficient inspections, work instruction and maintenance, the opportunity to blend training into work processes with microlearning platforms is compelling. Empowering frontline workers to access training on demand drives productivity and quality. Training in the flow of work saves on time away from the job and makes critical information available at the point of need. Making training more accessible, engaging and relevant builds a work culture of continuous learning that benefits both the workforce and the business.
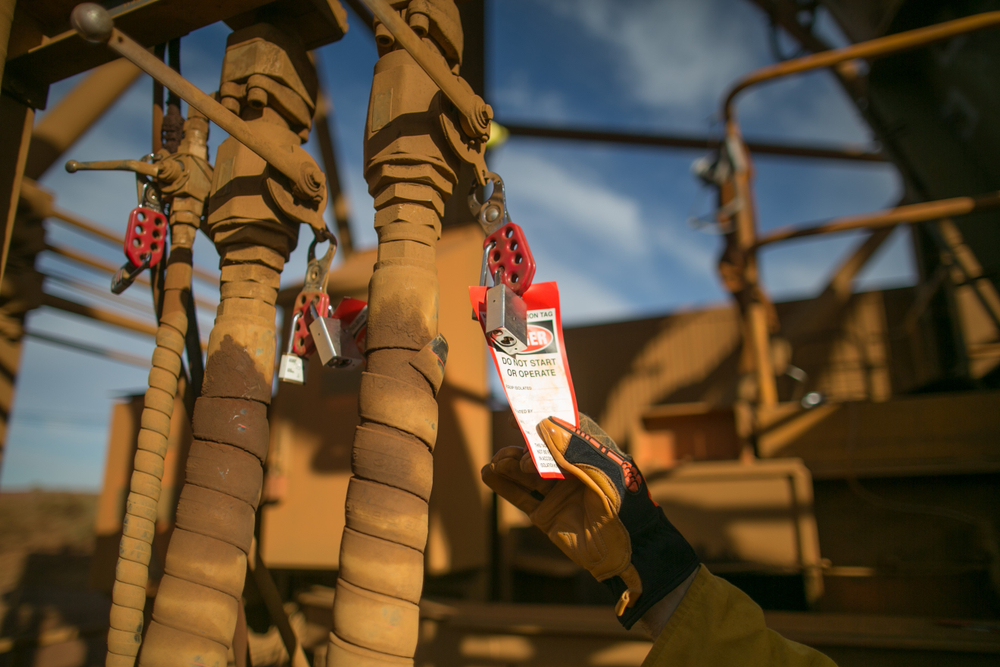
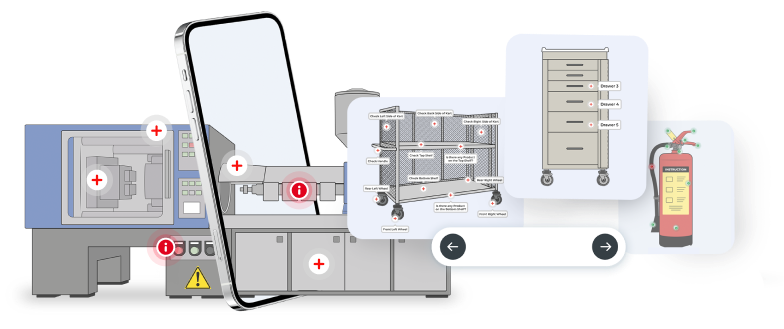
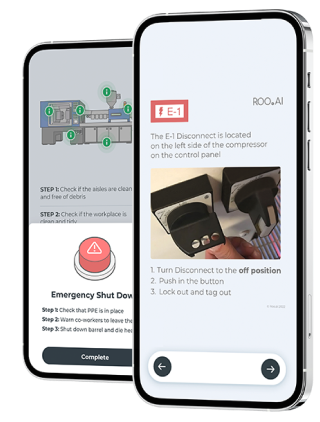
Ensuring Safety and Compliance with Digitalized Lock Out – Tag Out Processes
In industrial settings, where machinery and equipment pose inherent hazards, implementing robust lockout-tagout (LOTO) procedures is crucial for safeguarding the well-being of workers. In the realm of industrial safety, the lockout-tagout (LOTO) process stands as a cornerstone for preventing accidents during equipment maintenance and servicing. To optimize safety and compliance, organizations must adhere to best practices for executing LOTO processes effectively. With the advent of digital work instruction solutions on mobile devices, LOTO best practices can be more effectively enforced in several ways.
Enforcing Standardization
Digitalizing LOTO processes allows for the standardization of safety protocols, minimizing human error and ensuring consistency. Enabling workers with digital tools can enforce predefined workflows and procedures, guiding workers through the steps required to safely isolate energy sources and apply lockout devices. By standardizing LOTO procedures, organizations can mitigate the risk of procedural deviations that can increase the risk of accidents.
Continuous Training and Education
Ensuring ongoing training and education on LOTO procedures is crucial to reinforce knowledge and skills. Modern digital frontline platforms such as ROO.AI offer the opportunity to embed training and safety reminders in the flow of work, providing the workforce with in-context learning opportunities. Along with offering easier access to safety training on demand, digital frontline tools can facilitate improved toolbox talks, and scenario-based training exercises to help reinforce the importance of LOTO compliance and safety-consciousness.
Enhanced Documentation and Compliance
Digitalization facilitates comprehensive documentation of LOTO procedures, improving monitoring and compliance with regulatory requirements. Digital lockout-tagout workflows enable organizations to automatically capture equipment information, procedural verification using images and video, and generate digital audit trails of LOTO activities. This digitized documentation not only enhances accountability but also simplifies regulatory reporting and compliance assessments, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties and fines.
Digitalize LOTO Best Practices
Digitalizing lockout-tagout processes offers a transformative approach to enhancing workplace safety, efficiency, and compliance. By leveraging digital solutions to automate procedures, reinforce safety training and improve documentation, organizations can elevate safety standards, reduce risks, and foster a culture of safety excellence. As manufacturers strive to embrace digital transformation initiatives, digitalizing LOTO processes emerges as a critical enabler for achieving safety objectives and safeguarding employee well-being in industrial environments.
Manufacturing Safety Audit Checklist
Download our free PDF Safety Audit Form, or Get a Live Demo to discover how we incorporated this checklist into an easier, faster mobile app with visual assistance to guide the inspection. Customize inspections and work instructions to your exact equipment and manufacturing processes to boost safety and compliance with regulations.
Warehouse Safety Inspection Checklist
Digitalization in Oil & Gas by the Numbers
Growth Prospects
- The global upstream industry will invest over $500 billion and generate over $800 billion in free cash flows in 2024. (3)
- 81X The increase in unconventional oil and gas productivity due to technology over the last decade. (6)
- 60% of oil and gas executives expect digital technologies and AI to change their businesses significantly by 2030. (2)
- $5 per barrel of oil equivalent (BOE) captured for upstream companies through digitalization initiatives in exploration, well management and maintenance. (1)
Workforce Challenges
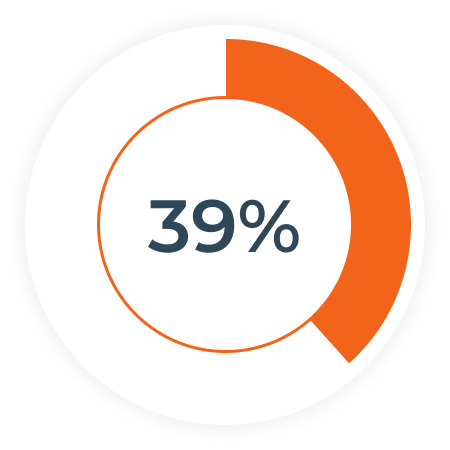
Oil and gas companies in North America are having difficulty finding frontline workers. (2)
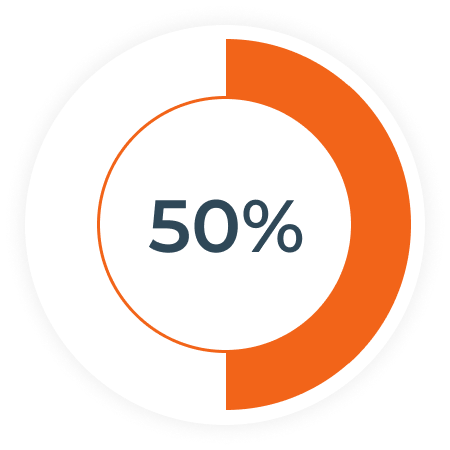
the percentage of the existing workforce in oil and gas that is expected to retire within the next 7 years. (5)
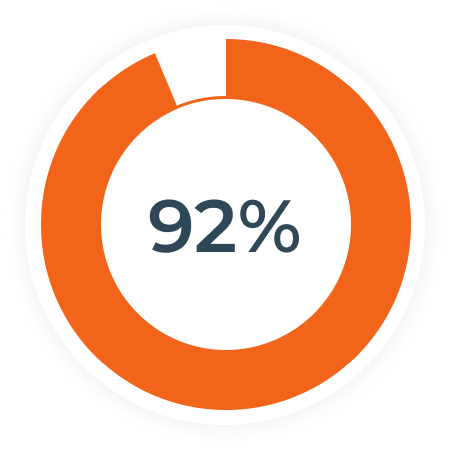
of oil and gas executives say reskilling the workforce will be critical to company success going forward. (6)
Energy Transition

oil and gas executives cite operational efficiency gains and direct emissions reductions as key metrics for assessing energy transition progress. (3)

oil and gas executives look to adjacent products such as natural gas, carbon capture, biofuels and hydrogen as key to their low-carbon investment strategies.

oil and gas executives say digital technologies to improve efficiency are among their top investments for decarbonization initiatives. (7)
Supporting Data
Keys to Achieving Workforce GMP Compliance
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are an essential foundation for successful manufacturing companies. To uphold these practices effectively, companies must establish robust systems and procedures. Among the critical elements of GMP is ensuring and validating workforce compliance with established policies. However, the implementation of these validation processes often comes with significant challenges for manufacturers.
Building on a Solid Foundation
A major focus for quality management professionals is the creation, approval and maintenance of policies and procedures for GMP. Comprehensive documentation is vital for GMP compliance. Developing detailed Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) is a cornerstone of GMP best practices, but the foundation for GMP documentation extends across all aspects of the company.
From company quality goals to full assessments of risks and responses to the development and production of products to guidelines for suppliers and commitments to customers, all procedures and processes should be well-documented. This documentation is critical to implementing GMP and serves as an important level of evidence of compliance, but GMP compliance is not just about written procedures. Compliance depends on the practical implementation of those procedures in daily operations.
Top Challenges of Workforce GMP Compliance
Even with the most thorough documentation, consistent GMP compliance can be difficult to achieve and maintain. Manufacturers must manage the interaction of people, production, equipment, facilities, suppliers and customers and the ripple effect of any changes. Regular maintenance and calibration of systems, facilities, and equipment are imperative for GMP compliance, along with supplier audits and ongoing customer feedback. However, supporting and validating workforce compliance poses certain unique challenges that are often difficult to address for manufacturers.
Developing and Validating Job Competence
One of the primary challenges in workforce GMP compliance is ensuring that all employees are adequately trained and aware of GMP policies. Training programs should ensure all personnel understand their roles in maintaining GMP standards. Too often, training is considered a job-shadowing experience, or solely an onboarding activity, which may not adequately support GMP success. And, employee turnover, experienced workers retiring, or the introduction of new staff can degrade GMP compliance practices as well.
Regular communication updates should be utilized to keep employees continuously informed about changes in procedures, regulations, and industry best practices. Refresher courses, and on-the-job, interactive training methods can help maintain a well-informed workforce. It is also essential to verify the completion of training programs and the practical application of GMP principles in daily tasks. Implementing competency assessments, layered process audits (LPA) and conducting periodic skill evaluations in real-world scenarios are vital steps in validating workforce compliance
Enforcing and Validating SOPs
The existence of SOPs is not enough; they must be actively enforced and implemented. Beyond training frontline workers, a framework to ensure adherence to the SOPs is what can deliver the best outcomes. Regular monitoring and supervision are essential to verify compliance, and any deviations should be promptly addressed through corrective actions. In addition, it is important to look for differences between locations, teams or shifts, across processes and at handoffs. Variations in procedures and practices may lead to compliance gaps
Along with enforcement comes the companion requirement for regular validation of SOPs to confirm that they are both effective and in compliance with GMP standards. This involves assessing the outcomes of processes, identifying any deviations, and implementing corrective actions. Continuous improvement is key, and feedback from the workforce, suppliers and customers should be considered in the validation process.
Integrating GMP into Every Process
Quality should not be an afterthought, but an integral part of the workflow on the frontline. Workforce tasks at each stage of the manufacturing process should prioritize GMP. This is particularly challenging given that the typical manufacturing workforce operates in a world of paper SOPs and training. With the advances in digital tools, manufacturers should seek out ways to modernize their frontline workers’ access to digital guidance and information that assists adherence to SOPs and GMP processes.
Frontline workers should also be empowered to identify and address issues that may compromise GMP. Here again, modern digital tools can enhance workforce abilities to both spot and communicate issues as they arise. These tools can also incorporate on-the-spot guidance and micro-training to ensure adherence to GMP. In addition, integrating GMP into the daily workflow of frontline workers promotes a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
After All the Planning, it Depends on People
In addition to equipment and processes, manufacturing is powered by people. The workforce plays a pivotal role in GMP compliance, but resistance to change or lack of employee engagement can impede compliance efforts. Manufacturers can address this challenge by fostering a culture of GMP ownership, recognizing, and rewarding compliance efforts, and involving workers in the decision-making processes related to GMP policies.
The workforce may view GMP compliance as an additional burden in the production process. Not only does this challenge manifest itself in the continuity of training, but also in tasks directly related to GMP compliance validations. Language and cultural differences may introduce additional obstacles. The key is to simplify and streamline compliance practices, considering the time and effort required by the workforce as partners in the delivery of GMP.
Taking a Digital Approach to Ensure Workforce GMP Compliance
While the journey toward workforce GMP compliance has many challenges, manufacturers can overcome these obstacles with thorough planning and proactive approaches that facilitate workforce adoption of GMP policies. Modern digital platforms specifically designed for frontline workers, like ROO.AI, deliver a significant boost for workforce GMP compliance.
ROO.AI’s advanced visualizations simplify and speed up inspections, safety checks, equipment maintenance, and LPA and other GMP audits while making it more visually intuitive to adhere to GMP standard operating procedures. Automating the data capture for GMP validation process also reduces time and effort for workers, addressing the resistance that additional quality steps may face from the workforce. Digitalizing the frontline empowers workers to be more proactive about identifying potential quality issues and communicating with their team and managers to make improvements. With ROO.AI, work instruction with access to micro-training can be accessed on-the-spot, training courses and updates delivered directly to workers as tasks, and completions and certifications tracked to ensure workforce job competency.
Ensuring workforce compliance with GMP is a multifaceted process that requires a comprehensive approach. By creating robust SOPs, enforcing and implementing them effectively, documenting processes meticulously, validating procedures regularly, and combining these efforts with a frontline digital platform to ensure understanding, adherence and accountability, manufacturers can prioritize quality at every stage of the manufacturing process to establish a strong foundation for GMP compliance.
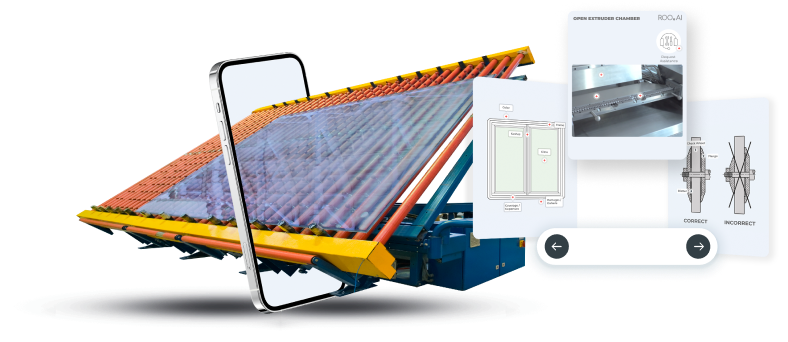
Improving Training and Safety for Frontline Workers in Oil Field Services
With the exposure to a wide variety of equipment and the dynamic, complex nature of oil field services operations, companies in the oil and gas industry have historically faced challenges in ensuring the well-being and competence of their frontline workforce. Frontline operator positions in the oil and gas industry are considered the third most dangerous of all frontline positions. With the ongoing departures of experienced personnel, oil field services companies are faced with a critical challenge in training and ensuring compliance with safety procedures as they replenish the frontline workforce.
In recent years, however, the adoption of digital technologies offers an unprecedented opportunity to enhance frontline worker training methodologies and safety protocols. A Draeger Safety study showed that using eLearning technologies reduced reported safety incidents by 46%. Advances in digital technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), wearables, AI and data analytics offer oil field services companies a transformative opportunity to develop a safer and more productive connected workforce with digitalized work instruction, inspections, safety and procedural training.
Revolutionizing Training with Digital Technologies
Digital Technologies are fundamentally changing training in several ways. One of the most significant advancements in training for frontline workers in oil field services comes from the ability of modern digital technologies to immerse the worker in the training content visually. Virtual reality (VR), in particular, places workers in simulated environments that replicate real-world equipment and operations. With virtual reality, workers can more effectively experience complex tasks and hazardous conditions to refine their skills in a risk-free environment.
In contrast, augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information into the physical world. This technology proves beneficial for on-the-job training, allowing workers to access relevant data and instructions while performing tasks. While both VR and AR are in the early phases and still quite expensive, innovative visualization technologies on standard mobile devices are also available.
These new lower-cost approaches combine the benefits of mobile, on-the-spot training with highly visual representations of information that are more easily and quickly understood and can be embedded into standard work instructions to provide ongoing reminders. These digital advances contribute to more effective and engaging training, ensuring that frontline workers are better prepared to navigate the challenges they may face in the field.
Tailoring Training with Data and Analytics
Digital technologies also enable the customization of training, addressing specific job roles and operational contexts. Data and analytics play a pivotal role in this customization process by adapting training to the specific needs of the operator and analyzing historical data to identify patterns and trends.
Furthermore, ongoing data analysis allows for continuous improvement in training methodologies. By monitoring workers’ performance metrics using digitalized SOPs, inspections and maintenance work orders, oil field services companies can identify areas that may require additional training or support, leading to a proactive approach to addressing potential safety and operational issues. This iterative process ensures that training programs remain dynamic and responsive to the evolving needs of frontline workers.
Interactive, Micro-learning Delivery
Digital technologies facilitate a shift from traditional, classroom-style training to interactive and micro-learning delivery of training. Through immersive simulations, workers can experience realistic scenarios and practice decision-making under pressure. This type of interactive training proves invaluable in preparing frontline workers for the unpredictable nature of oil field operations.
Mobile digital technologies also change the script of classroom training by providing training at the point of need in small, specific installments. Referred to as micro-learning, this approach has been documented to be 5-10 times more effective than conventional training with retention rates up to 60% higher. By digitalizing work instructions and inspections typically used by frontline workers, oil field services companies can embed safety and process training opportunities into the work processes not only facilitating access to the training but also ensuring and monitoring delivery and consumption.
Real-Time Monitoring and Wearable Devices
In addition to transforming training, digital technologies can also offer real-time monitoring capabilities through the deployment of wearable devices and sensors. These devices track various metrics, including workers’ health and environmental conditions, or locations and proximity to hazards.
Real-time monitoring enables immediate response to emergencies, ensuring that frontline workers receive timely assistance in the event of accidents. Wearable devices are also used as a preventive measure to alert workers and supervisors to potential hazards based on real-time data, allowing for proactive risk mitigation.
Making the Transition Accessible, Affordable and Effective
Oil Field Services companies have a growing number of digital alternatives they can leverage to improve safety and operational efficiency for their frontline workforce. ROO.AI is partnering with oil field services companies to digitalize common, critically important frontline processes such as field maintenance, rig up and rig down operations, equipment and site safety checks, and equipment repair and return to service. By enabling the concepts discussed, such as visualization, personalization and microlearning, ROO.AI is helping innovative companies in the oil and gas industry to upskill the workforce and cultivate a culture of safety. Applying digital technologies like ROO.AI ensures that frontline workers are not only well-trained but also equipped with the tools and knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of oil field services efficiently and safely.
Key Frontline Metrics That Boost Production Quality
Frontline workers are the foundation of many manufacturing companies’ production process, and their activity is crucial in enhancing product quality. The precision and accountability of the frontline workforce directly influence production quality, making it essential to establish and monitor key quality metrics.
In addition, recent studies like one by the American Quality and Productivity Center (APQC) highlighted that reducing rework and scrap could add back over 2% to manufacturer’s profitability. Data like this creates a further incentive for quality management programs to look for ways to expand their impact on the frontline. Recognizing the critical role of frontline workers in shaping production quality is the first step toward implementing a comprehensive quality management system.
To achieve this, it is essential to track and measure specific frontline quality metrics that directly impact production quality. Furthermore, making these metrics clear and visible to the frontline workforce enables workers to participate in the effort to drive higher quality. This is a critical element of an effective Quality Metrics program. A Deloitte study found that metrics that create the impression of tracking worker activities were perceived by 15% of workers as demotivating, and the same study found that as much as 32% of worker time shifted to performative work that just gave the impression of productivity.
Engaging workers in the selection and measurement of quality metrics can deliver a much more effective program that will be more widely adopted and supported by the frontline workforce. While the emphasis and focus of these metrics might vary in relation to the products and manufacturing processes of a specific manufacturer, the core concepts at the foundation of these metrics are very relevant to frontline activities across industries.
First Pass Yield
Measuring the percentage of products manufactured correctly without the need for rework or repair is a critical metric for frontline operations. The metric sheds light on whether production processes are efficiently and consistently delivering quality outputs. Monitoring First Pass Yield enables manufacturers to identify areas of improvement in their processes, machinery, or workforce training, ensuring that products meet quality standards from the outset.
Defect Rate
While First Pass Yield measures the relationship between efficiency and quality, Defect Rate measures the overall quality levels of the production process. Monitoring and minimizing defect rates are paramount in ensuring customer satisfaction, reducing production costs associated with rework or scrap, and maintaining high levels of product quality. A lower defect rate signifies a higher level of precision and consistency across all aspects of production, contributing to the overall excellence of manufactured products.
Scrap and Rework Rate
Understanding the scrap and rework rates provides visibility into the costs of poor quality, as well as, visibility into many aspects of the manufacturing process. Tracking this metric helps manufacturers to identify defect trends and look for the root causes of defects, allowing for targeted improvements in processes, materials, or training to minimize waste and enhance overall quality.
Schedule Realization
Schedule realization measures the ability of a manufacturing facility to meet schedule or delivery goals which in turn directly impacts quality by meeting customer expectations. High schedule realization rates indicate that the production schedule is being effectively managed, contributing to overall operational efficiency and quality..
Tracking Employee Training and Certification Rates
Ensuring the continuous training and certification of frontline employees is essential for maintaining and improving production quality. Well-trained workers not only make fewer errors, but they are also more adept at spotting potential issues that can affect quality. Providing regular training opportunities ensures that employees stay current with critical skills used on the frontline and the current manufacturing processes that the company has set as standards. A skilled and knowledgeable workforce is a cornerstone of high-quality.
Key Steps For Success
Engaging the frontline in the program is a key to success. Tap frontline supervisors and visible leaders in the workforce to help define the program, while using the opportunity to discuss the importance of setting measurable quality goals for frontline workers. Emphasize the value of establishing current state baselines and benchmarking against industry standards or best practices. This also offers an opportunity to set targets with buy-in from the frontline workforce.
Equally critical to success is the ability to ensure standardized inspection processes and to quickly and easily capture the required data. Introduce tools and technology that will simplify the process for the frontline to ensure adoption and consistent use. Platforms such as ROO.AI are critical in guiding workers through standardized inspections and automating collection of data so that quality metrics programs for the frontline are not perceived as slowing production or creating unnecessary work.
Finally, use the initiative to provide the frontline workforce with the opportunity to contribute to continuous improvement efforts that boost quality. Provide visibility of quality metrics to frontline workers and build into the process, preferably within the digital platforms, an easy way to suggest improvements or identify possible root causes of quality issues. Make these contributions visible across the workforce, potentially with recognition and rewards, to increase worker engagement. Utilizing program design and launch to reinforce training initiatives for frontline workers is also an opportunity not to be missed.
Informed Workers Are A Key To Quality
Frontline workers are the driving force behind production quality, and the implementation of key quality metrics can help them make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement. By embracing frontline quality metrics and implementing enabling digital platforms for quality inspections and data collection, manufacturers can empower their frontline workforce to enhance production quality, reduce defects, and deliver products that meet and exceed customer expectations. This approach not only results in higher customer satisfaction but also boosts efficiency, productivity and competitiveness in the market.
Innovator in Flowback and Sand Management Innovates the Frontline
EnerCorp is a leading provider of engineered solutions for the oil and gas industry.
Known for its innovations in eFlowback and Sand Management equipment, EnerCorp infuses innovation into every aspect of the company, driving to deliver better, faster, more effective approaches in technology, safety, operations and customer service.
Modernizing Pre and Post Job Inspections
With competition and costs increasing, the company was looking for modernization opportunities. EnerCorp’s innovative equipment was in high demand, and enabling accurate visibility to equipment inventory was a key to maximizing revenue opportunities across operating locations. Fast and efficient equipment turn-round was also a pivotal factor in meeting customer demand and increasing EnerCorp’s return on capital. Ensuring maintenance crews were able to consistently identify and document the condition of equipment post job was critical to EnerCorp’s ability to chargeback needed repairs to customers which would improve operating margins.
Looking for a frontline-optimized solution
EnerCorp’s team had already leveraged computerized solutions for the management of the equipment used to deliver services to their customers, but the team led by Aaron Kelver, US Asset Manager, was always on the lookout for opportunities to innovate. Aaron wanted to streamline the processes of pre and post job inspections which at the time was done with a system that was more appropriate for office workers. Rather than force frontline workers or supervisors to document the inspection in an office, after the fact, Aaron wanted to use mobile devices to digitalize the process and capture data and images on the spot. The goal was to make the system more efficient and frontline-friendly while building in standardization and training which the old system did not provide.
Live inside 90 days
EnerCorp set an ambitious target of replacing the existing software within 90 days. The team partnered with ROO.AI to model the equipment management system, the inspections, and the repair workflows for their high-volume Sahara Sand Separators. With a working framework, the project was expanded to the rest of the EnerCorp equipment inventory. Using ROO.AI’s agile implementation approach and the platform’s ability to make quick changes immediately available, Aaron’s team delivered a frontline-optimized solution across their eFlowback and Sand Separator product lines within 90 days.
- Mobile Pre and Post Job Inspections with embedded micro-training that reinforced standard operating procedures
- A cloud-based equipment management system that aggregated detailed information, documents, images, and recertification renewals while dynamically attaching every inspection for each unique asset
- Equipment transfers workflows and asset inventory reporting by status and location with data downloading to CSV for additional analysis
- Automatic generation of customer-ready documents with details and images from inspections and the automated collection and calculation of repair costs and labor hours
Gathering the data to better drive the business
With ROO.AI, EnerCorp’s frontline staff can use their mobile devices as they conduct inspections and repairs to document issues and verify equipment conditions. The standardized process is enforced through the ROO.AI app while data collection and report generation is automated to improve efficiency and accuracy. Equipment status and location are now immediately visible. With ROO.AI in place, Aaron is seeing more opportunities to use the data to identify preventable issues and understand the real costs of maintenance and repairs to help reduce equipment downtime, lower maintenance expenses, and improve return on capital.